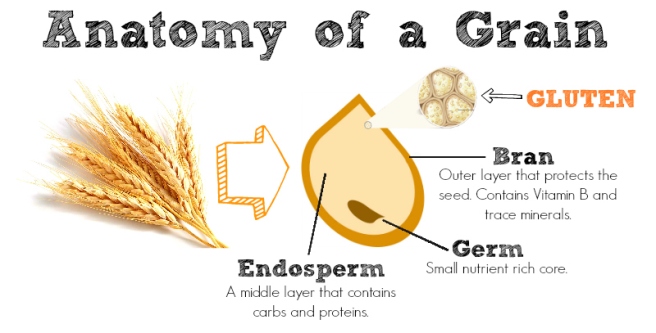
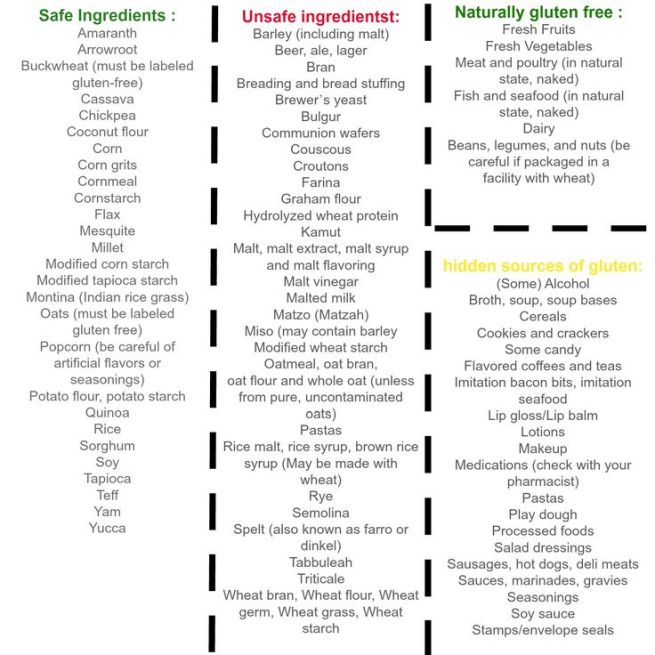
What is gluten sensitivity?
Gluten sensitivity is very different in celiac disease in that there is no biological harm done to the body (specifically the microvilli of the small intestine) when ingesting gluten. A gluten intolerant person will feel gastrointestinal discomfort when consuming gluten, but with no harm done to their small intestines.

What are the symptoms of gluten sensitivity?
The characteristics of gluten sensitivity are the same as celiac disease, minus the small intestine damage.

What is the difference between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?

Source:
Gratix, Niki. (2013, August 29). Retrieved from http://www.cortjohnson.org/blog/2013/08/29/celiac-disease-gluten-sensitivity-and-chronic-fatigue-syndrome-pt-1-misdiagnosis-and-mortalit/
Gluten sensitivity. (2016). Retrieved from https://www.gluten.org/resources/getting-started/gluten-sensitivity/